Content

They often take the services of online or traditional brokerage firms or advisors for investment decision-making. Equipment means table, chair, cabinet, computer, copier, calculator, fax machine, telephone, computer, etc. used in offices and stores of the business.
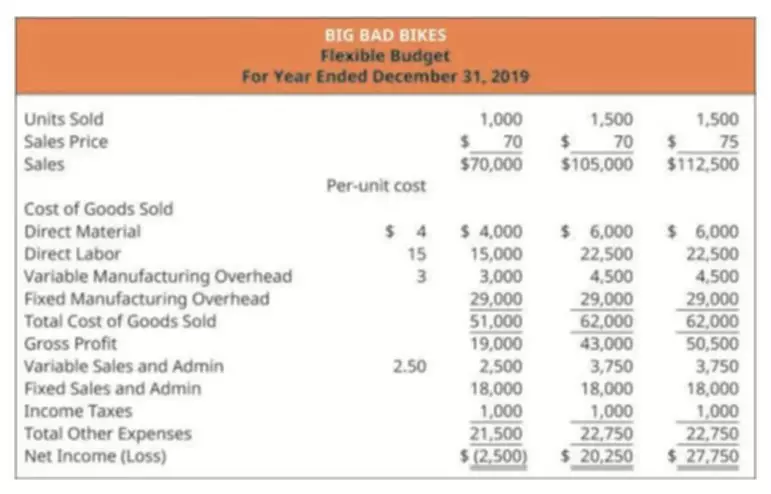
The total assets are equal to the total liabilities and owner’s equity. Typical long-term financial liabilities include loans (i.e., borrowings from banks) and notes or bonds https://www.bookstime.com/ payable (i.e., fixed-income securities issued to investors). Liabilities such as bonds issued by a company are usually reported at amortised cost on the balance sheet.
Merits and Demerits of Balance Sheet Classification
Throughout this series of financial statements, you can download the Excel template below for free to see how Bob’s Donut Shoppe uses financial statements to evaluate the performance of his business. The owner/officer debt section simply includes the loans from the shareholders, partners, or officers of the company. This section gives investors and creditors information about the source of debt and more importantly an insight into the financing of the company.
How are liabilities usually classified on a balance sheet?
Liabilities are generally classified on a balance sheet as: tangible liabilities and intangible liabilities.
Keep in mind a portion of these long-term notes will be due in the next 12 months. Thus, this portion is always reported in the current section. Cash EquivalentsCash equivalents are highly liquid investments with a maturity period of three months or less that are available with no restrictions to be used for immediate need or use.
Company
Record here investment tax credits utilized as reduction of tax liabilities, when the carrier exercises the option to defer such credits for amortization over the service life of the related equipment. Record here the total noncurrent liability applicable to property obtained under capital leases. Subaccounts to this account shall be established to record balances pertaining to passenger and cargo transportation sold, respectively, and separately to sales in scheduled and non-scheduled services. Record here all accounts payable within one year which are not provided for in accounts 2000 to 2021, inclusive. Record here the total cost to the air carrier incurred in connection with modification, conversion, or other improvements to leased buildings and equipment.
Define solvency and discuss how this information might be useful in assessing the company’s solvency position. Discuss at least 2 situations in which estimates could affect the usefulness of information in the balance sheet. Discuss the usefulness and limitations of the information displayed on the balance sheet. It is also helpful to predict future cash generation, companies’ liquidity, and overall financial performance. Retail InvestorA retail investor is a non-professional individual investor who tends to invest a small sum in the equities, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and other baskets of securities.
Classified Balance Sheet: Definition & Example
Think office buildings, construction equipment, computers, farmland, or long-term stocks. Assets can also be categorized based on how you use them in your business. Operating assets are ones you use regularly, for the primary purpose of your business.
This account includes all building improvements, including upgrades made to building wiring for technology. If buildings are acquired by gift, the account reflects their fair value at the time of acquisition. 232 Accumulated Depreciation on Buildings and Building Improvements. Accumulated amounts for the depreciation of buildings and building improvements.
Like your unclassified balance sheet, the totals of these classifications must follow the accounting equation, detailed below. Most accounting software applications allow you to choose what type of balance sheet you wish to produce, though if you have multiple assets or liabilities you need to properly track, you may want to skip the unclassified balance sheet altogether. For internally generated intangible assets, IFRS require that costs incurred during the research phase must be expensed. Costs incurred in the development stage can be capitalized as intangible assets if certain criteria are met, including technological feasibility, the ability to use or sell the resulting asset, and the ability to complete the project. All items of income and expense recognised in a period must be included in profit or loss unless a Standard or an Interpretation requires otherwise. [IAS 1.88] Some IFRSs require or permit that some components to be excluded from profit or loss and instead to be included in other comprehensive income. That information, along with other information in the notes, assists users of financial statements in predicting the entity’s future cash flows and, in particular, their timing and certainty.
- A copy of Carbon Collective’s current written disclosure statement discussing Carbon Collective’s business operations, services, and fees is available at the SEC’s investment adviser public information website – or our legal documents here.
- Current assets include cash and items that can be converted to cash in the coming year; current liabilities are due in the same time frame.
- The valuation account is used to adjust the value in the trading securities account reported on the balance sheet.
- The right side of the balance sheet details the company’s obligations and shareholders’ equity.
- This section gives investors and creditors information about the source of debt and more importantly an insight into the financing of the company.
- Earned revenue, determined by the yield or average fare method or by the sales-lift-match method, shall be consistently and periodically cleared by debit to this account, and by credit to the appropriate profit and loss revenue account.
Property, plant, equipment, long-term investment, and intangible assets. A business organization enjoys the utility classified balance sheet of fixed assets for more than a year. The balance sheet includes assets and liabilities & owner’s equity.
For example, Current Assets could include classes for cash and cash equivalents, inventory, assets held for sale and prepaid expenses. Liabilities could include accrued expenses, accounts payable, tax liabilities and liabilities held for sale. On a balance sheet, assets are reported on the left-hand side or at the top of the sheet, depending on the format you’re using. Then, liabilities and owners’ equity are listed on the right, or following the assets. Assets are listed in order of how quickly you think you’ll use them up, with current assets at the top and fixed assets at the bottom. Similarly, current liabilities are listed first, followed by long-term liabilities.

Every one of the resources of the organization are introduced on the asset report on the left side. The right side of the balance sheet details the company’s obligations and shareholders’ equity. Getting a clear view of your company’s assets will help you keep things running smoothly, seek investment, and get a bird’s-eye view of the financial health of your business. Understanding your assets at a glance will empower you with the fiscal information to make the best decisions possible.
BTC may be the latest or last chance to get rich in this era. It will reach $200000 next year or the next year.
BTC has increased 20 times in the last year, and other coins have increased 800 times!!!
Think about only $2 a few years ago. Come to the world’s largest and safest virtual currency exchange Binance to Get free rewards. Don’t miss the most important opportunity in life!!!
https://hi.switchy.io/91xl